Internet/broadband connectivity is a major issue nowadays, especially in developing nations, for it has an impact on their economic growth. It is true that broadband speeds, which is measured in Mbps, is not consistent, as there are nations where speeds are particularly fast and high, while there are still many places around the world where the connection is still slow. Akamai released the statistics based on their research for the third quarter of 2016, showing the countries with fast broadband speeds. Included in the top 10 are the following places:

In terms of average connection speed, the top 10 ranking is a bit skewed, with the United States not in the top 10, while Norway gets included, as follows:
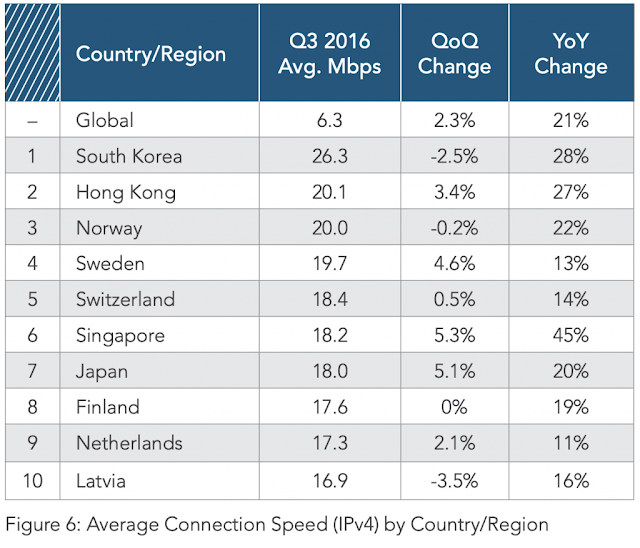
Based on this statistic, you can see that most of these countries have established economies. Globally, the average broadband speed is 6.3 Mbps for the third quarter of 2016. Akamai collected the data from 200 different countries during their survey. It is noticeable that the higher broadband connection speeds are in Scandinavian and a handful of Asian countries and cities.
Broadband connectivity has a significant effect on many economic sectors, particularly the ICT sector. It can promote innovation and growth in the specific industry and likewise, contribute to the other areas of the economy via increased productivity. Broadband also improves the quality of life through job growth. It facilitates the distribution of information and ideas that can lead to the development of and competition for new business models, processes, and new products. Its multiplier effect can drive employment growth, productivity, and GDP several notches up. Today, a number of business broadband options are out there.
Thailand's study of implementing a Broadband Policy in 2010 projected that if this is applied, the penetration of broadband technologies in the country (by 2015) will double, with 80% of it being wireless. This could lead to the expansion of the domestic economy, attract new investments, and raise the GDP by nearly 2.4% annually.
From these examples alone, you can see how broadband connectivity can impact the economies of developing countries. Not only that; it also has an effect on households, individuals, businesses, and a variety of other sectors. In New Zealand, many subscribers are opting for uncapped data plans. However, there are several broadband plans available, and there are many providers, such as Bigpipe that offer various packages to complement your Internet usage and your lifestyle.
- South Korea
- Hong Kong
- Norway
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Singapore
- Japan
- Finland
- Netherland
- Latvia

In terms of average connection speed, the top 10 ranking is a bit skewed, with the United States not in the top 10, while Norway gets included, as follows:

Based on this statistic, you can see that most of these countries have established economies. Globally, the average broadband speed is 6.3 Mbps for the third quarter of 2016. Akamai collected the data from 200 different countries during their survey. It is noticeable that the higher broadband connection speeds are in Scandinavian and a handful of Asian countries and cities.
Broadband Connectivity, Internet access, and development
In one study conducted in Africa, it has been noted that Broadband connectivity and Internet access greatly affects the economy of the continent. According to the World Bank, developing countries enjoy a 1.4% growth in GDP for every 10% growth in broadband access. About 80 new jobs are created each time there are 1,000 new broadband Internet subscribers. The implementation of the Broadband Policy for South Africa in July 2010 is expected to generate 28,000 new jobs in five years. How to get the internet in remote areas.Broadband connectivity has a significant effect on many economic sectors, particularly the ICT sector. It can promote innovation and growth in the specific industry and likewise, contribute to the other areas of the economy via increased productivity. Broadband also improves the quality of life through job growth. It facilitates the distribution of information and ideas that can lead to the development of and competition for new business models, processes, and new products. Its multiplier effect can drive employment growth, productivity, and GDP several notches up. Today, a number of business broadband options are out there.
Access to Online Education
Broadband connectivity allows many developing nations to have access to online education and training, increasing the number of educated individuals, who are more likely to be interested in furthering their education or applying what they have learned in developing micro and macro businesses. In the Caribbean and Latin America, the growth of broadband access from 2007 to 2008 contributed about US$6.7 billion and US$14.3 billion to some 24 countries in this region, while the contribution to the region's GDP was 3.4% from 2009 to 2010.Thailand's study of implementing a Broadband Policy in 2010 projected that if this is applied, the penetration of broadband technologies in the country (by 2015) will double, with 80% of it being wireless. This could lead to the expansion of the domestic economy, attract new investments, and raise the GDP by nearly 2.4% annually.
From these examples alone, you can see how broadband connectivity can impact the economies of developing countries. Not only that; it also has an effect on households, individuals, businesses, and a variety of other sectors. In New Zealand, many subscribers are opting for uncapped data plans. However, there are several broadband plans available, and there are many providers, such as Bigpipe that offer various packages to complement your Internet usage and your lifestyle.
Comments
Post a Comment